웹 개발 메모장
3. Pytorch nn과 nn.functional 본문

필요 패키지
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F문서
- nn
https://pytorch.org/docs/1.0.1/nn.html - nn.functional
https://pytorch.org/docs/1.0.1/nn.html#torch-nn-functional
nn 과 nn.functional
제공하는 기능들은 비슷한데 사용하는 방법에 차이가 있습니다.
nn 이 제공하는 기능들
- Parameters
- Containers
- Conv
- Pooling
- Padding
- Non-linear Activation
- Normalization
- Recurrent
- Linear
- Dropout
- Sparse
- Distance
- Loss
- Vision
- Data Parallel
- Utilities
- ...
nn.functional 이 제공하는 기능들
- Conv
- Pooling
- Non-linear Activation
- Normalization
- Linear function(=fully connected layer)
- Dropout
- Loss
- Vision
- ...
conv2d의 사용
nn 과 nn.functional의 차이를 conv2d를 이용해서 알아봅시다.
nn.conv2d
nn.functionnal.conv2dtorch.nn.Conv2d VS torch.nn.functional.Conv2d
입력 이미지에 2d Convolution을 적용시키는 메소드 입니다.
torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True)torch.nn.functional.conv2d(input, weight, bias=None, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1)nn.Conv2d
weight를 직접 선언해주지 않음
in_channels: input image 채널의 수out_channels: convolution 결과 채널의 수kernel_size: convolution 커널의 크기(필터 크기)
torch.nn.functional.conv2d
weight를 직접 선언 ( 외부에서 만든 filter를 사용 )
input: input Tensor ( minibatch×in_channels×iH×iW )weight: 필터의 shape ( out_channels × groups in_channels × kH × kW )
예제
아래 그림과 같은 convolution 연산을 pytorch로 진행해 보겠습니다.
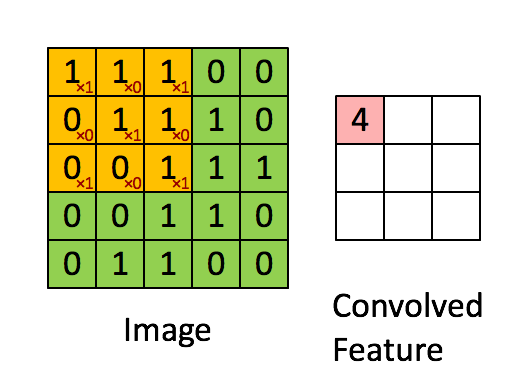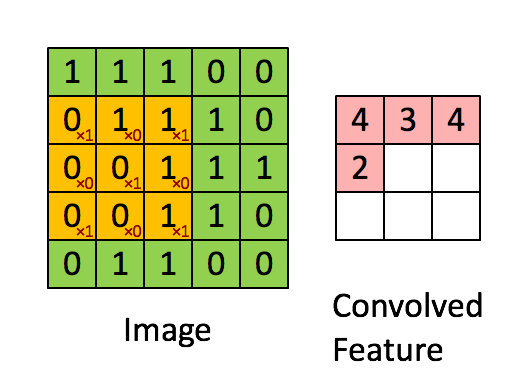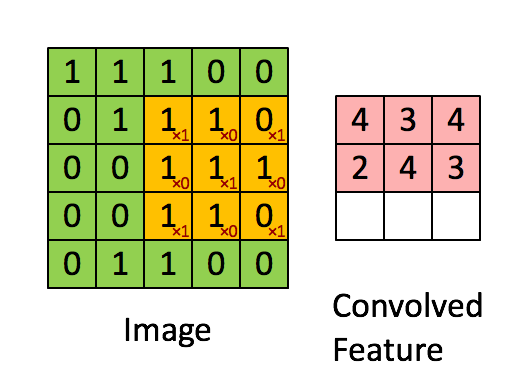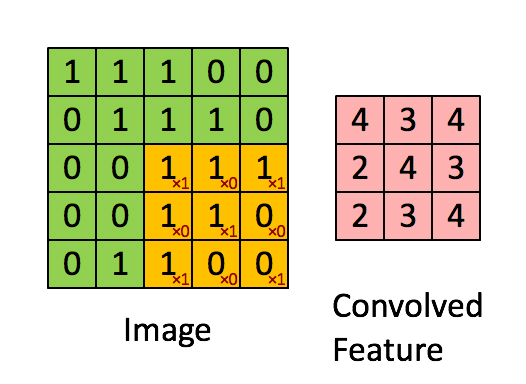
1. torch.nn.functional.conv2d
이미지와 같은 input, filter 텐서를 생성하고 conv2d 메소드로 연산한 코드와 결과입니다.
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.autograd import Variable
import numpy as np
input = torch.Tensor(np.array([[[
[1,1,1,0,0],
[0,1,1,1,0],
[0,0,1,1,1],
[0,0,1,1,0],
[0,1,1,0,0]
]]]))
filter = torch.Tensor(np.array([[[
[1,0,1],
[0,1,0],
[1,0,1]
]]]))
input = Variable(input, requires\_grad=True)
filter = Variable(filter)
out = F.conv2d(input, filter)
print(out)tensor([[[[4., 3., 4.],
[2., 4., 3.],
[2., 3., 4.]]]], grad_fn=) [Finished in 0.5s]2. torch.nn.conv2d
nn.conv2d는 weight를 제공해 주기 때문에 filter를 넘기지 않았습니다.
결과 출력 뿐만 아니라 사용된 weight도 같이 출력하겠습니다.
(호출할 때마다 결과가 달라집니다.)
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.autograd import Variable
import numpy as np
input = torch.Tensor(np.array([[[
[1,1,1,0,0],
[0,1,1,1,0],
[0,0,1,1,1],
[0,0,1,1,0],
[0,1,1,0,0]
]]]))
input = Variable(input, requires_grad=True)
func = nn.Conv2d(1,1,3)
print(func.weight)
out = func(input)
print(out)Parameter containing:
tensor([[[[-0.0219, 0.0051, 0.0586],
[ 0.1440, 0.3288, -0.2014],
[ 0.0100, 0.1854, -0.1580]]]], requires\_grad=True)
tensor([[[[ 0.0342, 0.3050, 0.5113],
[-0.2727, 0.2196, 0.4731],
[-0.0924, 0.4095, 0.5477]]]], grad_fn=) [Finished in 0.5s]
'옛날.. > pytorch' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 6. 신경망 학습과 평가 (0) | 2019.07.22 |
|---|---|
| 5. 신경망 정의와 순방향 전파 (0) | 2019.07.22 |
| 4. Pytorch torchvision에서 데이터셋 가져오기 (0) | 2019.07.21 |
| 2. Pytorch autograd와 Variable (0) | 2019.07.21 |
| 1. Pytorch 소개 (0) | 2019.07.21 |
Comments